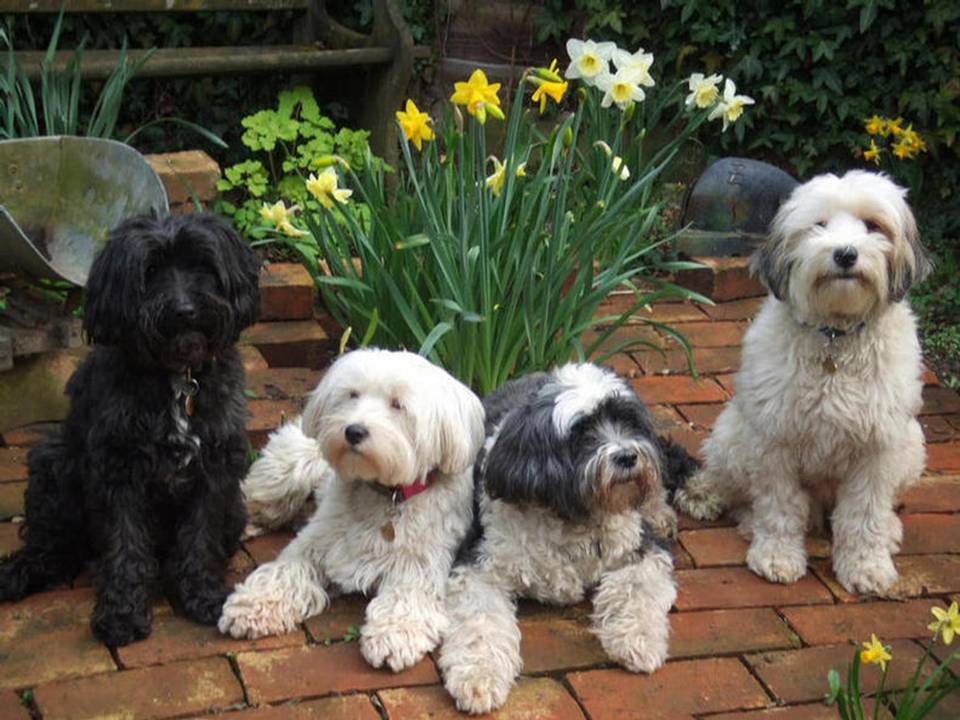
The “Holy Dog of Tibet,”
The Tibetan terrier dog, often called the “Holy Dog of Tibet,” is an ancient breed with deep ties to Tibet’s spiritual, cultural, and geographical heritage. Despite its name, it is not a true terrier but a non-sporting breed. Its history spans over 2,000 years, rooted in Tibetan monasteries, the harsh Himalayan environment, and the spiritual practices of the Tibetan people. From its origins in Tibet to its modern role as a cherished companion, the Tibetan Terrier’s story is one of survival, spirituality, and cultural exchange.
Origins in the Tibetan Highlands
The Tibetan Terrier’s history begins in the high, rugged plateaus of Tibet. This region is known for its extreme climate and high altitude. Monks and nomadic herders bred these dogs for their agility, endurance, and resilience. Their thick, double-layered coat protected them from the cold, while their compact, medium-sized bodies helped them navigate rocky terrain. They developed large, flat feet that acted like natural snowshoes, giving them balance on snowy and uneven surfaces.
Westerners called them terriers, but they are not related to the hunting terrier group. Instead, Tibetan Terriers served as watchdogs, herders, and companions. They guarded homes and monasteries, herded sheep, and even retrieved lost items along cliffs.
Spiritual and Cultural Significance
Tibetan Terriers held a special place in Tibetan culture. Tibetan monks, or lamas, considered them sacred and called them “Luck Bringers.” People did not sell or breed them commercially. Instead, they gifted them to bring good fortune. Families believed these dogs protected them from evil spirits and misfortune.
The breed also connected deeply with Buddhist philosophy. Monks revered all life, and the loyal Tibetan terrier earned their respect. These dogs lived alongside monks in monasteries, never used for hard labour like pulling carts or hunting. Their long, flowing coats and calm demeanour suited the tranquil monastic lifestyle.
Legends say Tibetan Terriers guided travellers through the treacherous Himalayan mountain passes. Their keen sense of direction and agility made them ideal for navigating dangerous terrain. Travellers believed the dogs offered divine protection, serving as both physical and spiritual guides.
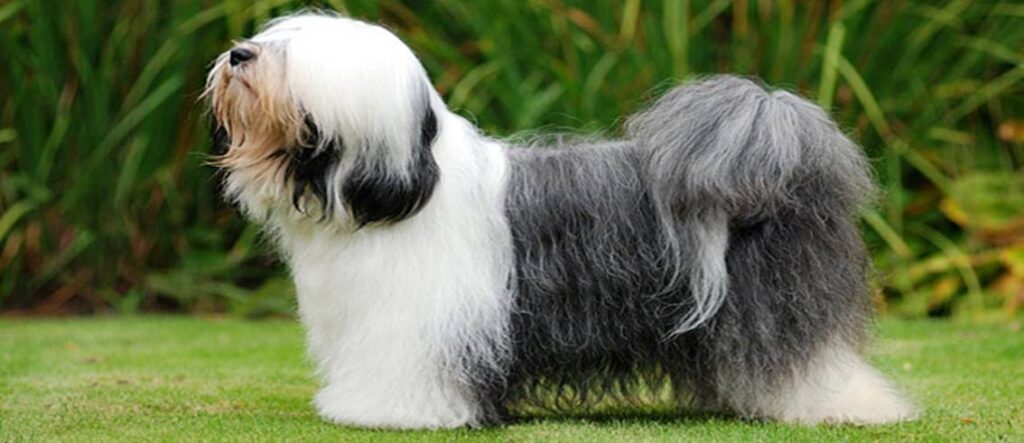

Introduction to the Western World
For centuries, Tibetan Terriers remained unknown outside Tibet due to the region’s isolation and the breed’s cultural significance. In the early 20th century, they began reaching the Western world, where they gained recognition as a distinct breed.
Dr. Agnes Greig, a British physician stationed in India in the 1920s, played a key role in introducing the breed to the West. After treating a Tibetan woman, Dr. Greig received a Tibetan terrier dog as a gift. Impressed by its loyalty, intelligence, and resilience, she brought several dogs to England and started breeding them. In 1937, the Kennel Club in the United Kingdom officially recognized the breed.
By the mid-20th century, the breed gained popularity in the United States. In 1973, the American Kennel Club (AKC) recognized the Tibetan terrier dog as part of the Non-Sporting Group. Today, people cherish the breed for its friendly personality and unique history.
Physical and Temperamental Characteristics
The Tibetan terrier dog is a medium-sized dog, standing 14 to 17 inches tall and weighing 20 to 30 pounds. Its most distinctive feature is its long, double-layered coat, which comes in colours like black, white, gold, or tricolour. This coat protected the breed from harsh Tibetan winters and remains a key trait today.
Temperamentally, Tibetan Terriers are friendly, intelligent, and adaptable. They thrive in active families or more sedentary lifestyles. Their loyalty and social nature make them excellent companions. However, they can be independent and stubborn, a trait rooted in their self-reliant origins in the Tibetan wilderness.
Conclusion
The Tibetan Terrier’s rich history reflects its adaptability, intelligence, and spiritual significance. As “Holy Dogs of Tibet,” they served as protectors and guides, cherished by monks and nomads. Today, they continue to embody loyalty, resilience, and a strong bond with humans. Their story, blending spirituality, cultural heritage, and survival, makes them one of the world’s most fascinating dog breeds.