Dog Man’s Best Friend
Dogs have long held the title of “man’s best friend,” and this is not a coincidence. The loyalty of dogs is a defining trait that has fascinated and endeared them to humans for thousands of years. From ancient myths to modern tales of heroism, dogs have consistently demonstrated an extraordinary bond with humans that goes beyond simple companionship. This incredible loyalty stems from a combination of evolutionary, biological, and emotional factors, making dogs one of the most devoted and reliable creatures on Earth.
A History of Loyalty
The relationship between dogs and humans is one of the oldest animal-human partnerships. It dates back over 15,000 years when early humans began domesticating wolves. These early wolves, who later evolved into modern dogs, were initially drawn to human campsites for food, and in turn, provided protection and assistance in hunting. Over time, this mutually beneficial relationship strengthened, and dogs became indispensable to human societies. They provided not just utility but also companionship and loyalty.
Many ancient cultures celebrated dogs for their unwavering fidelity. In Greek mythology, the three-headed dog Cerberus was considered the loyal guardian of the underworld. In Egyptian culture, dogs were often buried alongside their owners, a testament to their place in the afterlife as companions. Even today, dogs continue to play essential roles in various human cultures, not just as pets but as working animals, serving in law enforcement, search and rescue, and therapy.
The Science Behind Canine Loyalty
While the deep bond between humans and dogs is undeniable, there are also scientific reasons behind a dog’s loyalty. One of the most critical factors is oxytocin, commonly referred to as the “love hormone.” This hormone is responsible for social bonding in many species, including humans. Studies have shown that when dogs interact with their owners—through petting, playing, or even just looking into their eyes—both the dog and the human experience an increase in oxytocin levels. This creates a positive feedback loop, reinforcing the bond between the two.
Another key aspect of canine loyalty lies in their evolutionary history. Dogs are pack animals, descended from wolves, which have a highly social structure cantered around a pack leader. Over millennia, dogs have transferred this pack mentality to their human
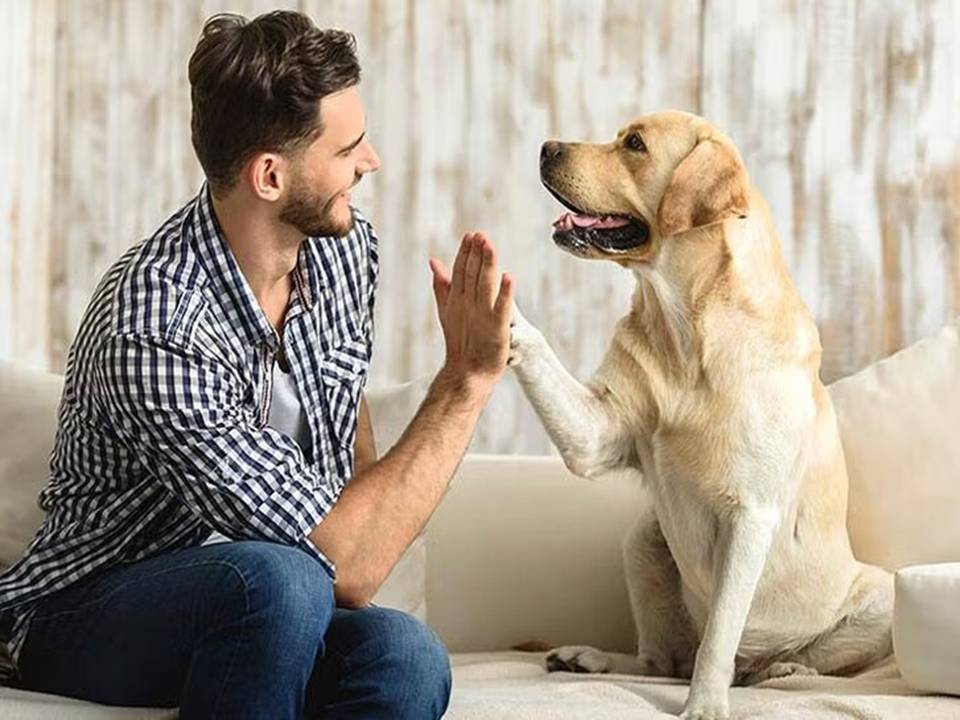

families. To a dog, their human owner often takes on the role of the pack leader, and dogs instinctively show loyalty to their pack leaders as part of their survival strategy. This loyalty is hardwired into their nature, leading them to protect, follow, and love their human companions unconditionally.
Emotional Connection and Empathy
Dogs are incredibly empathetic animals, often sensing their owners’ emotions and responding accordingly. Studies have found that dogs can differentiate between human emotions such as happiness, sadness, and anger by reading facial expressions and body language. This emotional attunement makes dogs particularly sensitive to their owners’ needs. Many dog owners have reported that their dogs seem to know when they are upset, offering comfort by sitting beside them or resting their heads in their laps.
The most famous stories of canine loyalty often involve situations where dogs have gone to great lengths to stay by their owners’ sides. One of the most well-known examples is the story of Hachiko, an Akita dog from Japan. Hachiko would wait for his owner at the Shibuya train station every day after work. Even after his owner passed away unexpectedly, Hachiko continued to wait at the station for nearly ten years until his own death. His devotion has been immortalized with a statue in his honour, symbolizing the profound loyalty dogs are capable of.
In another case, a dog named Capitan in Argentina made headlines for visiting his deceased owner’s grave every day for over seven years. These stories highlight not just a dog’s loyalty but also their emotional capacity to experience loss and longing, further solidifying their status as more than just pets.
Loyalty in Action: Working Dogs
Dogs’ loyalty is not just a matter of emotional bonding; it also translates into action. Working dogs, such as those in law enforcement, the military, or therapy, showcase their loyalty in ways that often involve risking their own lives for the sake of humans. Police dogs, for instance, are trained to protect their handlers in dangerous situations. Their courage and loyalty can be seen when they chase down criminals, assist in search-and-rescue missions, or sniff out explosives. Similarly, service dogs for individuals with disabilities are trained to perform life-saving tasks, such as alerting their owners to seizures or retrieving medication. Their dedication to their roles is driven by their innate desire to serve and protect their human companions.
Military dogs, such as those deployed in combat zones, also demonstrate extraordinary loyalty. These dogs form intense bonds with their handlers, often displaying incredible bravery in the line of duty. The story of Cairo, a Navy SEAL dog who played a key role in the mission to capture Osama bin Laden, exemplifies how dogs can be trusted with critical tasks that require both intelligence and unwavering commitment.
Conclusion
The loyalty of dogs is one of their most remarkable traits, one that has been nurtured over millennia through a deep, evolving relationship with humans. Whether acting as companions, protectors, or service animals, dogs consistently demonstrate an unparalleled devotion that enriches the lives of those who are fortunate enough to have them by their side. This loyalty is not just a product of training or domestication; it is a fundamental aspect of who dogs are as a species. Their ability to bond with humans, sense emotions, and offer unconditional love makes them truly incredible creatures and the epitome of loyalty in the animal kingdom.