The Catahoula Leopard Dog’s History
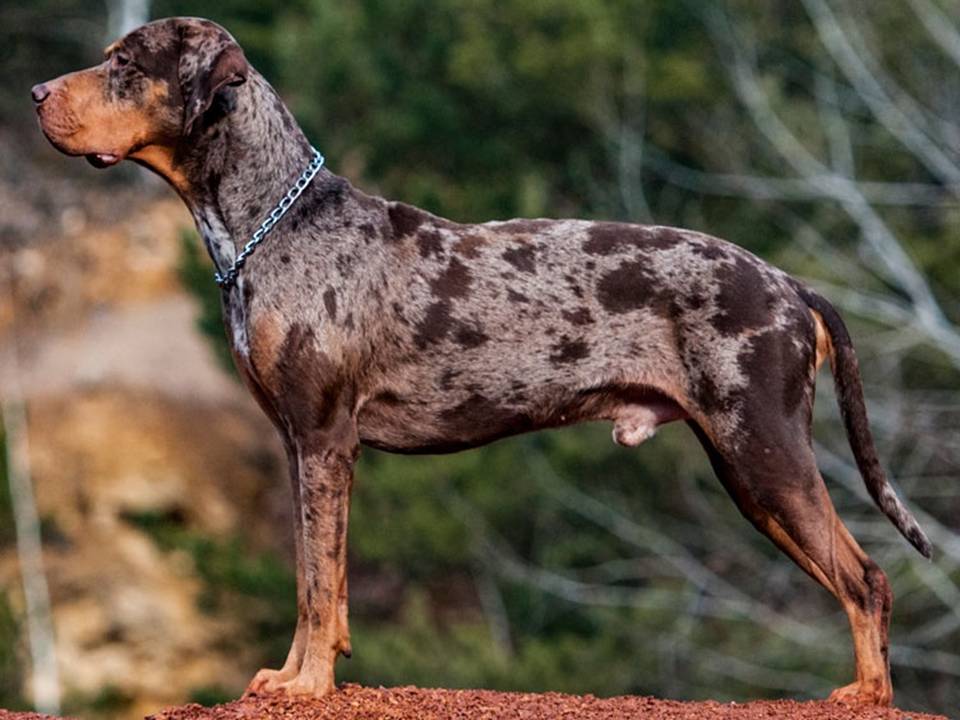
The Catahoula Leopard Dog, often called simply the Catahoula, stands out as one of America’s most unique and versatile dog breeds. Originating in Louisiana, this breed earns admiration for its intelligence, strong work ethic, and striking appearance. Known for its diverse coat colours and unique “glass eyes” (blue or multi-coloured eyes), the Catahoula has a rich history tied to the American South. Its lineage blends Native American culture, Spanish exploration, and early American settlers. By exploring the Catahoula’s history, we can better understand how it evolved into a highly valued working dog, especially for herding and hunting.
Early Origins: Native American and Spanish Influence
The Catahoula Leopard Dog’s history begins long before Louisiana became part of the United States. The breed’s name comes from Catahoula Parish in northern Louisiana. The word “Catahoula” likely originates from the Choctaw language, meaning “sacred lake.” Native Americans in this region kept dogs that helped them hunt and perform daily tasks. These dogs likely formed the foundation of the Catahoula breed.
In the 16th century, Spanish explorers arrived in the Americas. They brought various dog breeds, including Mastiffs, Greyhounds, and Spanish war dogs. Over time, these European dogs interbred with the native dogs of the Choctaw and other tribes. This mixing of Spanish and Native American dogs likely created the early ancestors of the Catahoula.
The blend of these genetic backgrounds produced a dog perfectly suited to Louisiana’s swampy, rugged terrain. The Catahoula emerged as a tough, resilient, and adaptable breed. Early settlers quickly recognized its value for hunting wild game, especially feral hogs, which were challenging to manage without a skilled and determined dog.
Development as a Working Dog
By the 18th and 19th centuries, the Catahoula had become a vital working dog in Louisiana. Farmers, hunters, and livestock managers relied on the breed for its herding and hunting skills. Unlike many herding breeds, the Catahoula did not rely on barking to control livestock. Instead, it used its physical presence and intelligence to manage animals, particularly wild hogs and cattle.
Catahoulas earned the nickname “hog dogs” because of their exceptional ability to track and herd wild boar. This practice remains common in some rural parts of the southern United States today. The breed’s independence, quick decision-making, and relentless determination made it ideal for handling feral livestock in the wilderness. Its strong herding instinct and problem-solving skills allowed it to manage even the most stubborn animals.
In addition to herding, Catahoulas excelled in hunting. They tracked not only hogs but also deer, raccoons, and squirrels. Their keen sense of smell, intelligence, and determination made them invaluable for people living off the land. The breed’s webbed feet, perfect for navigating Louisiana’s swampy terrain, further contributed to its success as a versatile working dog.
The Catahoula’s Role in American History
As the United States expanded westward in the 19th century, settlers from Louisiana brought their Catahoulas with them. These dogs gained a reputation outside Louisiana for their versatility and strength. They proved essential in managing livestock on the open plains, helping settlers adapt to new and challenging environments. Despite their widespread use, Catahoulas remained relatively unknown outside the Southern states for much of their early history.
The breed began to gain national recognition in the mid-20th century. In 1979, Louisiana designated the Catahoula as its official state dog. This recognition highlighted the breed’s importance to the region’s cultural and agricultural heritage. It also helped preserve the breed’s lineage and promote responsible breeding practices, as industrialization and changes in farming had caused its numbers to decline.

Unique Traits and Legacy
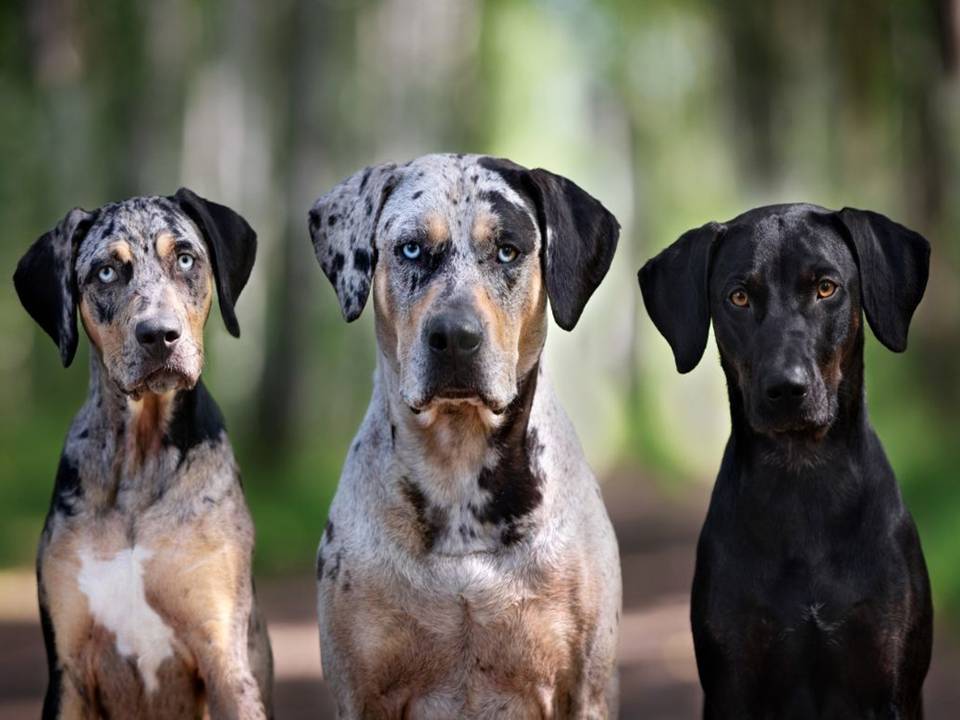
The Catahoula Leopard Dog’s appearance sets it apart from other breeds. Its coat often features a merle pattern, earning it the “leopard” nickname. Many Catahoulas also have striking blue or “glass” eyes, or heterochromatic eyes (each eye a different colour). These features add to the breed’s unique allure.
Beyond their looks, Catahoulas are celebrated for their intelligence, loyalty, and strong work ethic. They make excellent working dogs but also serve as loyal and protective family companions. However, their high energy levels, intelligence, and independent nature mean they thrive best in environments where they have jobs to do. Whether herding, hunting, or participating in dog sports, Catahoulas need plenty of mental and physical stimulation to stay happy and healthy.
Conclusion
The Catahoula Leopard Dog’s history is as unique and complex as the breed itself. Its roots trace back to Native American culture and Spanish exploration. Over time, it became a vital working dog in the American South. The breed’s distinctive appearance, combined with its herding and hunting abilities, has made it a beloved symbol of Louisiana’s rural heritage.
Today, the Catahoula continues to serve as a working dog in many parts of the United States. It is also gaining popularity as a loyal and energetic companion for active families. Through its long and storied history, the Catahoula remains a testament to the enduring bond between humans and their canine companions.