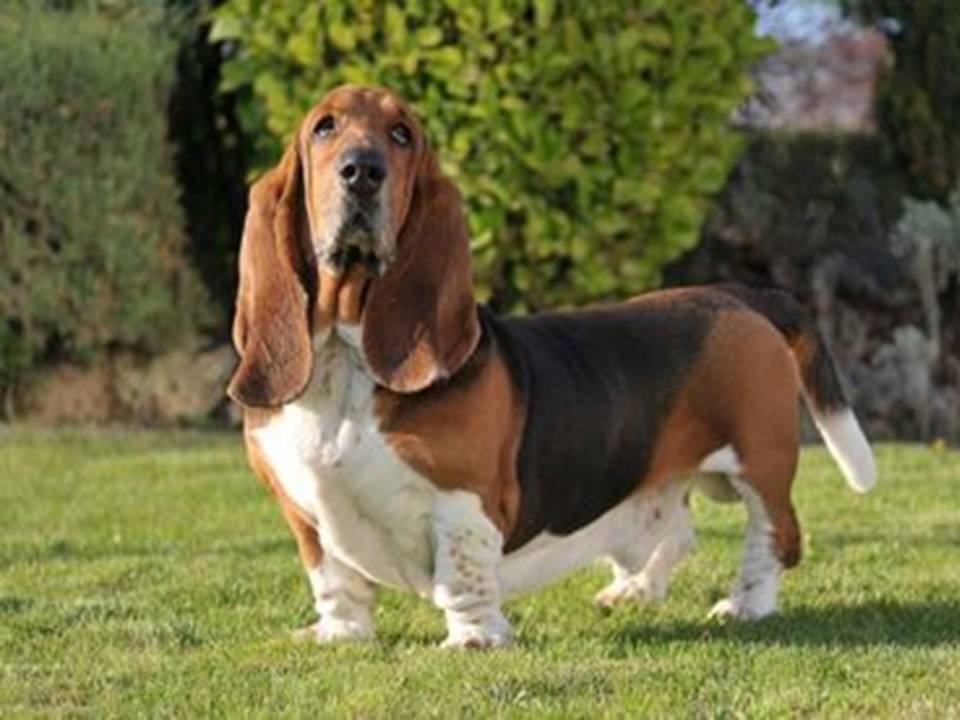
The French Basset Hound
The Basset Hound is one of the most recognized and beloved dog breeds. People know it for its long ears, droopy eyes, and low-slung body. While many see it today as a charming and gentle companion, the Basset Hound has a rich history rooted in hunting. Its origins trace back centuries, intertwining with French aristocracy, English breeding programs, and its evolution from skilled hunter to cherished pet.
Origins in France
The Basset Hound’s history begins in France. Hunters bred its ancestors to assist in hunting. The name “Basset” comes from the French word “bas,” meaning “low,” which describes the breed’s short legs and low stature. The Basset Hound belongs to the hound group, a category of dogs bred for their scent-tracking abilities. This trait made them invaluable in hunting, especially in France’s dense forests, where their keen sense of smell allowed them to track prey over long distances.
The earliest references to basset-type dogs date back to the 16th century, during the reign of French kings. At the time, hunting was a popular activity among the French aristocracy. Hunters used basset-type dogs to track small game like rabbits and hares. Their short stature helped them move easily through dense underbrush, and their slow pace suited hunters on foot. Before firearms became widely available, these dogs were especially useful because they could track and corner prey, allowing hunters to capture it.
The Development of the Modern Basset Hound
The Basset Hound we recognize today results from centuries of selective breeding. Early French basset-type dogs likely descended from the St. Hubert Hound, a breed developed by monks in the Ardennes region of Belgium and France. St. Hubert Hounds were famous for their exceptional scent-tracking abilities. Many consider them the ancestors of modern scent hounds, including the Bloodhound.
In the 19th century, the modern Basset Hound began to take shape. French breeders, including Count Le Couteulx de Canteleu, played a key role in refining the breed. They selected traits like long ears, loose skin, and a powerful sense of smell. These physical features enhanced the dog’s ability to capture scent particles from the ground and air, making them exceptional trackers.
The Father of the Basset Hound in England.
Sir Everett Millais, an English breeder, was one of the key figures in shaping the modern Basset Hound. Many call him the “father of the Basset Hound in England.” In the 1870s, Millais imported Basset Hounds from France to England, where he started a breeding

program to refine the breed further. His work, along with efforts from other British breeders, helped standardize the breed and establish its presence in England.
During this period, Basset Hounds appeared in dog shows, which were gaining popularity at the time. The breed’s unique appearance and calm temperament made it a favourite among dog fanciers, and its popularity grew. In 1882, the first Basset Hound Club formed in England, further cementing the breed’s place in the world of purebred dogs.
Role in Hunting
Even as the Basset Hound gained popularity as a show dog, its origins as a hunting dog remained central to its identity. Hunters prized Basset Hounds for their ability to track small game. Their short stature made them ideal for hunting in difficult terrain. Unlike faster, more aggressive hunting dogs, Basset Hounds worked at a slower pace, allowing hunters to follow on foot. Their long ears and loose skin helped trap scent particles, while their deep, booming bark allowed hunters to follow them even when out of sight.
One of the Basset Hound’s defining traits is its extraordinary sense of smell. The breed ranks second only to the Bloodhound in scent-tracking ability. Basset Hounds have around 220 million scent receptors in their noses, compared to humans, who have about 5 million. This makes them highly skilled at detecting and following scents over long distances, often across difficult terrain.
Though people no longer widely use Basset Hounds for hunting, their keen sense of smell remains one of their most defining traits. Even today, some use them in search-and-rescue operations or as detection dogs.
The Basset Hound in Popular Culture
In the 20th century, the Basset Hound transitioned from a working dog to a popular companion animal. Its distinctive appearance and calm, easy-going temperament made it a favourite in households worldwide. The breed became a popular subject in advertising and media, most famously in campaigns for the Hush Puppies shoe brand. The Basset Hound’s image represented the brand’s comfort and reliability, and this association boosted its popularity even further.
Basset Hounds have also appeared in television shows, movies, and cartoons. People often portray them as lovable, slightly lazy characters. Their laid-back nature and comical expressions have endeared them to audiences, solidifying their place as one of the most recognizable dog breeds.
Conclusion
The Basset Hound’s history blends aristocratic hunting traditions, careful breeding, and a transition into modern life as a beloved companion. From its origins in the dense forests of France to its rise in popularity in England and beyond, the Basset Hound has stayed true to its roots as a skilled scent-tracker with a calm and gentle demeanour. Today, people celebrate the Basset Hound not only for its history and abilities but also for its charm, making it a treasured pet for families worldwide.