Obesity for Dogs: One of the Most Common Health Issues
Obesity is not just a human problem; it also affects our beloved pets, especially dogs. As more dogs live in homes with plentiful food and less physical activity, obesity has become one of the most common health issues they face. Excessive weight can lead to severe health problems for dogs, including diabetes, joint issues, cardiovascular problems, and a shorter lifespan. As responsible pet owners, it is vital to understand the causes, risks, and solutions for keeping obesity at bay in dogs.
Understanding the Causes of Obesity in Dogs
Several factors contribute to dog obesity, many preventable with conscious effort.
Overfeeding: One of the most common reasons dogs become overweight is overfeeding. Whether it’s giving too many treats or feeding them calorie-rich food in excessive amounts, dogs can easily consume more than they need. Many commercial dog foods are high in calories and fats, and when paired with treats and table scraps, dogs quickly exceed their daily caloric requirements.
Lack of Exercise: Physical activity is essential for keeping dogs at a healthy weight. Many dogs, especially those living in urban environments, do not get enough exercise. Sedentary lifestyles, combined with overeating, lead to an accumulation of fat and weight gain over time.
Breed Predisposition: Certain dog breeds are more prone to obesity. Breeds like Labrador Retrievers, Beagles, Pugs, and Dachshunds tend to gain weight more easily due to genetics. Owners of these breeds need to be extra cautious with their dogs’ diets and exercise routines.
Age: As dogs age, their metabolism slows down, making it easier for them to gain weight. Senior dogs tend to be less active, which means they burn fewer calories, increasing the risk of obesity.
Spaying/Neutering: While spaying and neutering have numerous health benefits, these procedures can sometimes lead to weight gain, as they may reduce a dog’s metabolic rate. After being spayed or neutered, dogs often require fewer calories to maintain a healthy weight.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or Cushing’s disease, can lead to weight gain in dogs. If a dog is gaining weight despite a healthy diet and exercise routine, it’s important to consult a veterinarian to rule out any underlying health issues.
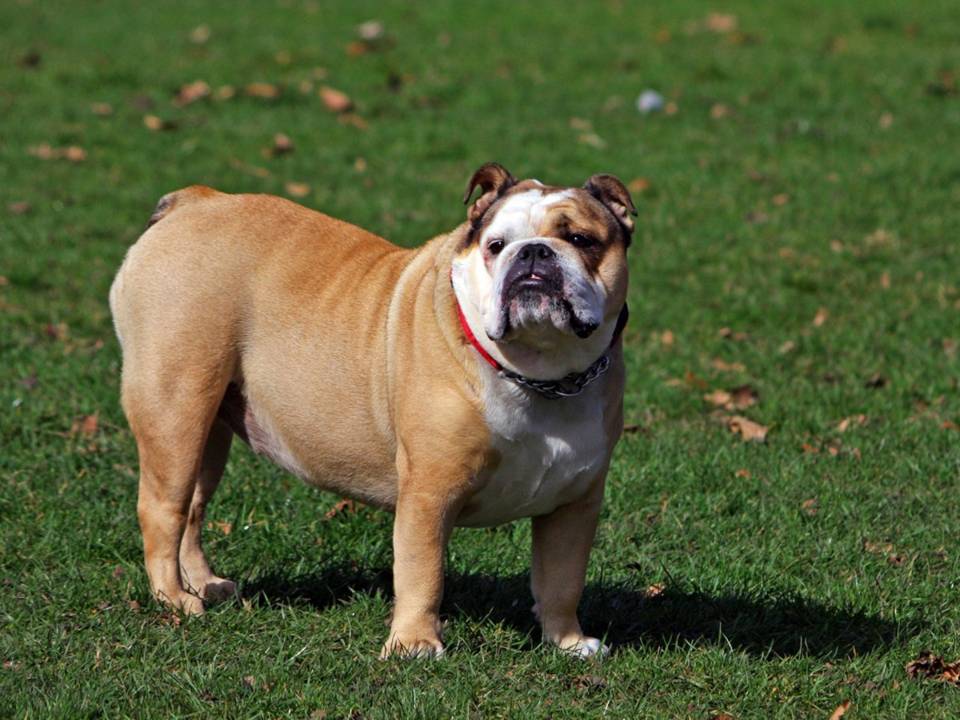

Health Risks Associated with Obesity
Carrying extra weight can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life. Obesity is more than just an aesthetic issue—it carries serious health risks that can shorten a dog’s life and reduce their overall well-being.
Diabetes: Obese dogs are more likely to develop insulin resistance, which can lead to Type 2 diabetes. Managing diabetes in dogs often requires strict dietary control, insulin injections, and frequent vet visits, all of which can be stressful for both the dog and the owner.
Joint and Mobility Issues: Excess weight puts added strain on a dog’s joints and bones, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis. Overweight dogs are more prone to injuries, such as torn ligaments, due to the additional pressure on their musculoskeletal system.
Heart Disease: Obesity can lead to cardiovascular problems in dogs, such as hypertension (high blood pressure) and heart disease. These conditions can severely impact a dog’s stamina, making it harder for them to enjoy activities like walking or playing.
Respiratory Problems: Overweight dogs often have trouble breathing, especially those with shorter snouts like Bulldogs or Pugs. Excess fat around the chest area can restrict the expansion of the lungs, leading to laboured breathing and a higher risk of respiratory issues.
Decreased Life Expectancy: Studies show that obese dogs have a shorter lifespan than their lean counterparts. The added strain on their bodies from carrying extra weight can lead to a reduced life expectancy, meaning owners may have less time with their beloved pets.
Preventing and Managing Obesity in Dogs
While obesity is a serious health issue, it is also highly preventable. With proper care and attention, owners can help their dogs maintain a healthy weight and avoid the risks associated with obesity.
Portion Control: Feeding the right amount of food is crucial. Many dog food packages provide feeding guidelines, but these are often too generous. Work with your veterinarian to determine the exact caloric needs of your dog, considering factors like age, breed, and activity level. Measure food portions carefully, and avoid free-feeding (leaving food out all day).
Quality Food: Not all dog food is created equal. High-quality, nutritionally balanced dog food can help maintain your dog’s health and weight. Look for foods rich in lean protein and fibre, while being low in unhealthy fats and artificial additives. Avoid feeding your dog table scraps, which are often high in calories and unhealthy ingredients.
Regular Exercise: Exercise is one of the best ways to prevent obesity in dogs. Daily walks, playtime, and activities like swimming or hiking can help burn off excess calories. Even older dogs need regular exercise to stay healthy, although their routines may need to be adjusted based on their mobility and stamina.
Limiting Treats: While treats can be a useful training tool, over-relying on them can quickly add up in terms of calories. Opt for low-calorie treats or offer healthy alternatives like small pieces of carrots or apples. When using treats for training, remember to adjust your dog’s main meals accordingly.
Monitor Weight: Regularly check your dog’s weight and body condition. Your veterinarian can help assess whether your dog is at a healthy weight and recommend adjustments to their diet or exercise routine if necessary. Some vets even offer weight management programs for overweight dogs.
Veterinary Check-ups: Regular visits to the vet can help detect any early signs of weight gain or obesity-related health problems. Your vet can provide tailored advice and support to help keep your dog healthy.
Conclusion
Obesity in dogs is a growing problem, but it is a preventable and manageable condition with the right approach. By controlling portions, feeding high-quality food, ensuring regular exercise, and being mindful of treat intake, pet owners can help their dogs stay at a healthy weight. Keeping obesity at bay not only prevents serious health risks but also improves a dog’s quality of life and longevity. A healthy dog is a happy dog, and with proper care, your furry companion can enjoy a long, active, and joyful life.