History and Origins of the Dachshund Sausage Dog
Dachshund sausage dog, often called the “Sausage Dog” because of its long, low body, has a rich history. This small but sturdy dog is famous for its unique shape, confident personality, and strong hunting instincts. Originally bred in Germany, the Dachshund has become one of the most beloved and recognizable dog breeds in the world.
Early Origins in Germany
The name “Dachshund” comes from the German words Dachs (badger) and Hund (dog). This name reflects the breed’s original purpose: hunting badgers. German hunters needed a dog that could chase and catch these fierce burrowing animals. The Dachshund’s long, low body made it perfect for this job.
The breed’s origins date back to the 15th century in Germany. Hunters wanted a brave, tenacious dog that could work in tough terrains and tight spaces. The Dachshund’s strong claws helped it dig, and its fearless nature allowed it to confront badgers and other small animals like rabbits and foxes in their dens.
Selective Breeding and Development
Over time, German hunters selectively bred Dachshunds to improve their hunting skills. By the 17th century, two sizes of Dachshunds had emerged: the standard size for hunting badgers and boar, and the miniature size for smaller game like rabbits.
Dachshunds were versatile hunters. They could work in packs to hunt larger animals and had an excellent sense of smell for tracking. Their ability to work both above and below ground made them stand out from other hunting breeds. This dual capability made them highly valued in the field.
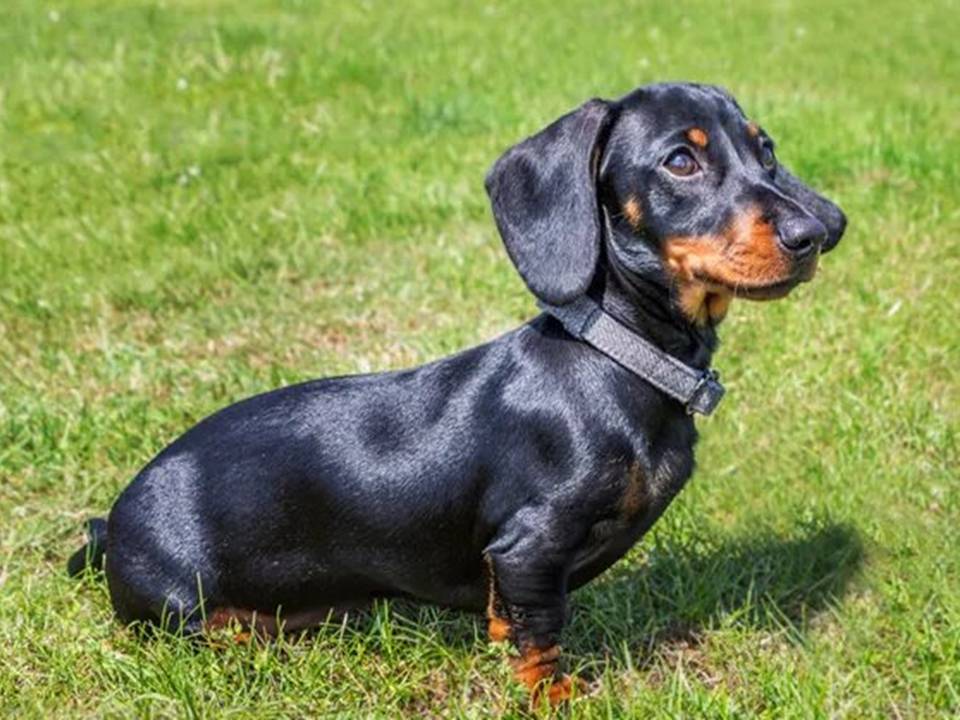

Physical Characteristics and Traits
Breeders carefully developed the Dachshund’s physical traits to support its hunting role. The long body and short legs allowed the dog to navigate tight underground spaces. Powerful jaws helped it hold onto prey, and loose skin protected it from bites and scratches. A deep chest provided greater lung capacity for stamina during long hunts.
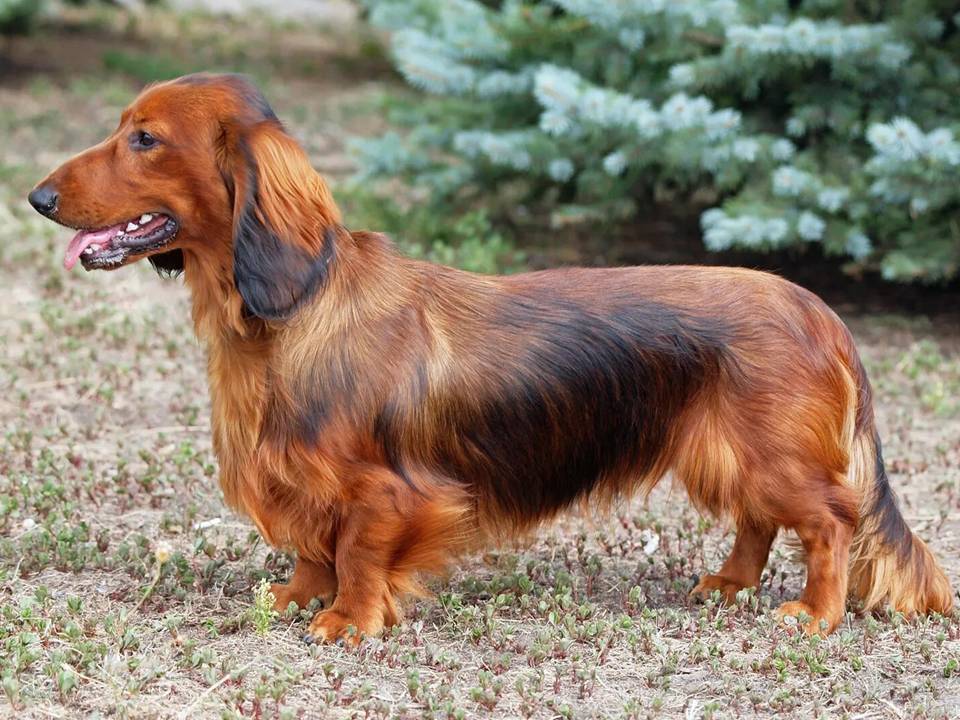
Dachshunds come in three coat types: smooth, wirehaired, and longhaired. Each coat had a specific purpose. The smooth coat is the most traditional. The wirehaired coat came from crossing Dachshunds with terriers for protection against rough undergrowth. The longhaired coat likely resulted from crossbreeding with spaniels, providing better insulation in cold climates.
Spread Across Europe and Beyond
In the 19th century, Dachshunds gained popularity outside Germany. European royalty and nobility, including Queen Victoria of England, took a liking to the breed. Queen Victoria’s love for Dachshunds helped spread their popularity in Britain. By the mid-19th century, Dachshunds were regulars at dog shows and exhibitions.
German immigrants brought Dachshunds to the United States. The breed’s adaptability helped it quickly gain favour in America. The American Kennel Club (AKC) recognized the Dachshund as an official breed in 1885, cementing its status.
Impact of World War I and World War II
The Dachshund’s German origins created challenges during World War I and World War II. Anti-German sentiment led to a decline in the breed’s popularity, especially in the U.S. and Britain. Some people saw owning a Dachshund as unpatriotic. The breed faced ridicule and negative propaganda, often portrayed as a symbol of Germany.
Despite these challenges, dedicated breeders in Germany, the UK, and the U.S. worked hard to preserve the Dachshund. By the mid-20th century, the breed’s popularity began to recover. Breeders highlighted the Dachshund’s charm, intelligence, and versatility as both a hunter and a companion.
Modern-Day Dachshunds
Today, the Dachshund is one of the most popular dog breeds worldwide. While most Dachshunds no longer hunt, they retain many traits from their hunting days. Their keen sense of smell, boldness, and tenacity remain, along with their distinctive physique.
Dachshunds are loyal, playful, and intelligent. They can be independent, a trait linked to their hunting history, but this independence sometimes makes them stubborn. Despite their small size, they have big personalities, which has won the hearts of dog lovers everywhere.
Conclusion
The Dachshund’s history shows its resilience, versatility, and adaptability. From its origins as a fearless badger hunter in Germany to its role as a beloved companion today, the breed has come a long way. Its physical traits reflect its hunting past, while its loyal and spirited nature keeps it a favourite in homes worldwide.
Today, the Dachshund symbolizes heritage and a remarkable journey through history. Whether as a hunter or a family pet, the Dachshund continues to charm people with its unique appearance and vibrant personality.