What You Must Know About Bernese Mountain Dog
The Bernese Mountain Dog is known for its tricolour coat, gentle nature, and strong work ethic. This breed has a long history, tracing back to the agricultural regions of Switzerland. Originally bred to assist farmers, the Bernese Mountain Dog has evolved into a beloved family companion.
1. Origins in Switzerland
The Bernese Mountain Dog, or Berner Sennenhund, comes from the Swiss Alps. It gets its name from the Canton of Bern. Switzerland has a history of breeding strong, resilient dogs suited for mountain life.
The Bernese Dog is one of four Swiss mountain breeds, known as Sennenhunds. The others include the Appenzeller, Entlebucher, and Greater Swiss Mountain Dog. “Sennenhund” means “herder’s dog,” highlighting its deep connection to farming.
Historians believe that the breed’s ancestors arrived in Switzerland with Roman soldiers over 2,000 years ago. These dogs, likely Mastiff or Molosser types, interbred with local farm dogs. Over time, this mix led to the development of the Bernese Mountain Dog.
2. Roles as a Working Dog
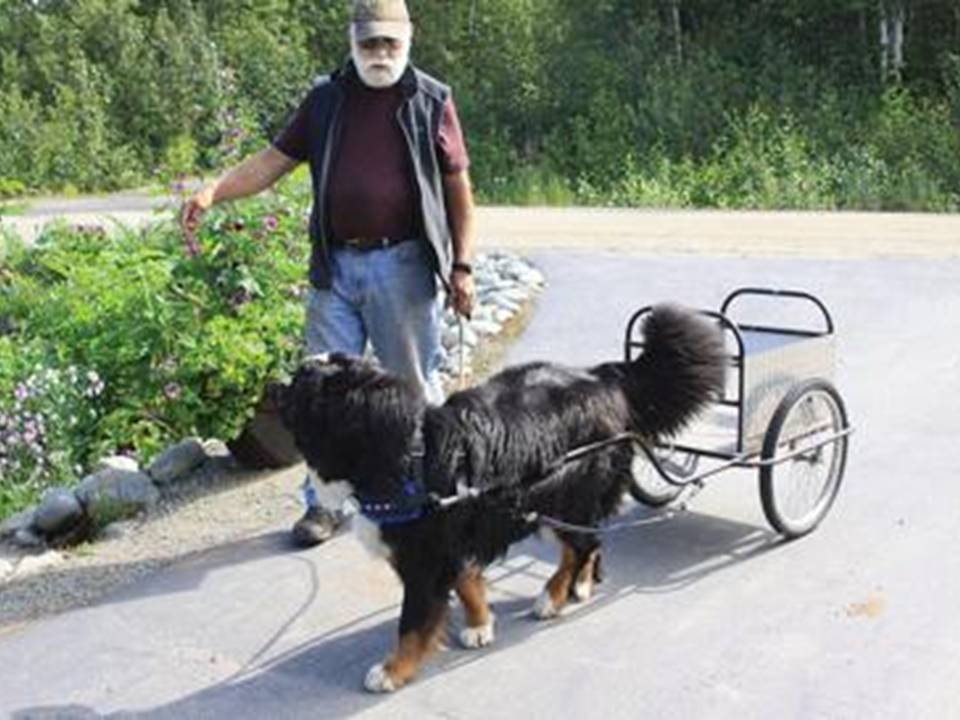
For centuries, the Bernese Dog played a key role on Swiss farms. Farmers relied on them for herding, guarding property, and pulling carts. These dogs transported milk, cheese, and other goods to market.
Their strength made them excellent cart-pullers. A team of Bernese Mountain Dogs could haul loads several times their weight. This made them vital for farmers who needed help moving heavy goods.
Besides their physical abilities, these dogs had a calm and dependable nature. They formed close bonds with families and were trusted to protect livestock from predators.
3. Decline and Resurgence
During the 19th century, industrialization reduced the need for working dogs. Machinery replaced cart-pulling, and improved fencing reduced the need for herding. The Bernese Dog population dropped, nearly leading to extinction.
Swiss dog enthusiasts saved the breed. In the early 20th century, Professor Albert Heim played a crucial role in its revival. He admired Swiss mountain dogs and worked to preserve them.
In 1907, Swiss breeders formed the first Bernese Dog club, the Schweizerische Dürrbäch-Klub. The breed was also known as the Dürrbächler, named after a village where they were common. The club focused on increasing numbers and refining breed standards.

4. International Recognition and Popularity
The Bernese Mountain Dog gained global attention in the early 20th century. By 1926, it arrived in the United States. In 1937, the American Kennel Club (AKC) officially recognized the breed.
Over time, its role shifted. Though still capable of farm work, the breed became a popular family pet. Its affectionate, loyal, and gentle nature made it a favourite among dog lovers.
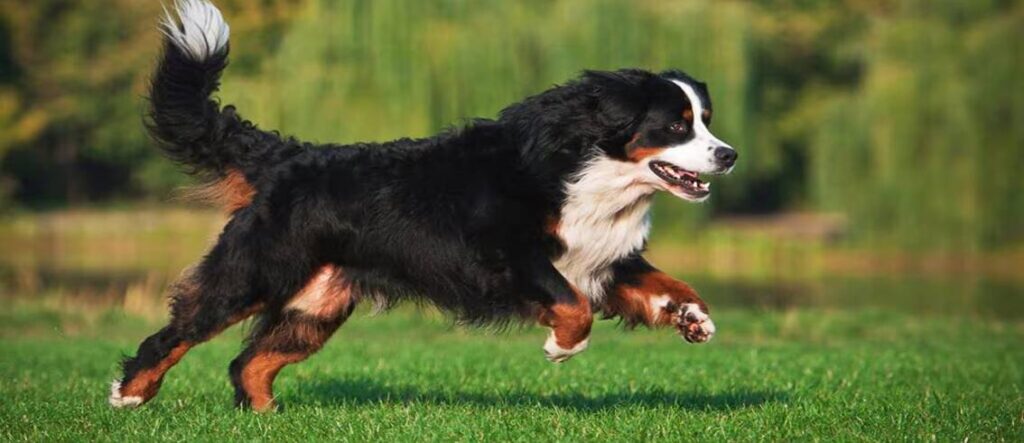
The breed also gained popularity in dog shows. Its glossy black coat, rust-coloured markings, and white chest made it a striking presence.
Even today, Bernese Mountain Dogs excel in various activities. They participate in cart-pulling competitions, therapy work, and canine sports. Their intelligence and trainability make them versatile companions.
5. Challenges and Preservation Efforts
Like many large breeds, the Bernese Dog faces health challenges. Common issues include hip and elbow dysplasia, bloat, and cancer. Sadly, their lifespan is short, averaging 7 to 10 years.
To improve the breed’s health, responsible breeders focus on genetic diversity. Many organizations, including the Bernese Mountain Dog Club of America, promote health testing and responsible breeding practices.
6. The Bernese Mountain Dog Today
Today, the Bernese Mountain Dog remains a beloved breed worldwide. Its farm days may be in the past, but its hardworking and loving nature lives on.
This breed thrives in family settings. Its calm, friendly temperament makes it great with children. Its loyalty ensures a strong bond with owners.
The Bernese Mountain Dog continues to honour its heritage. Whether in the Swiss countryside or a modern home, this dog remains a symbol of strength, devotion, and companionship.